In this article we’re exploring the fascinating realm of rocks and minerals that come alive under UV light. From the radiant hues of fluorite to the subtle shimmer of aragonite, each mineral tells a unique story of geological processes and chemical compositions. Prepare to be dazzled by nature’s own fluorescent UV light show!
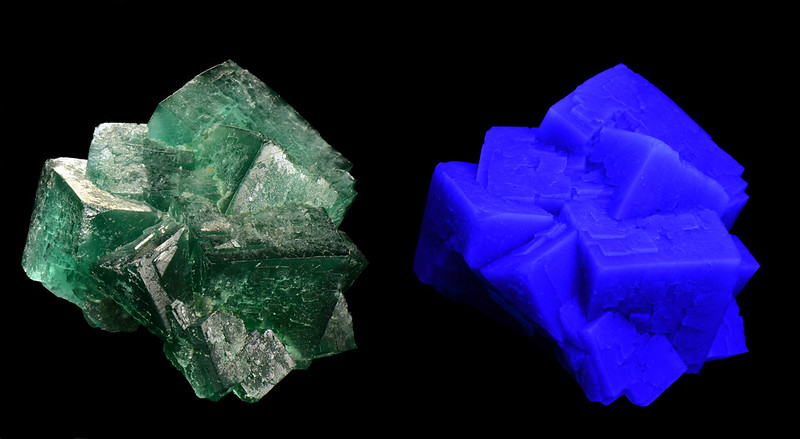
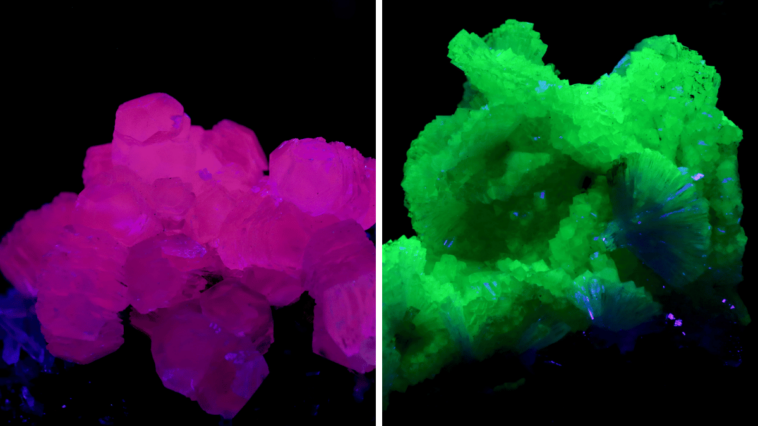
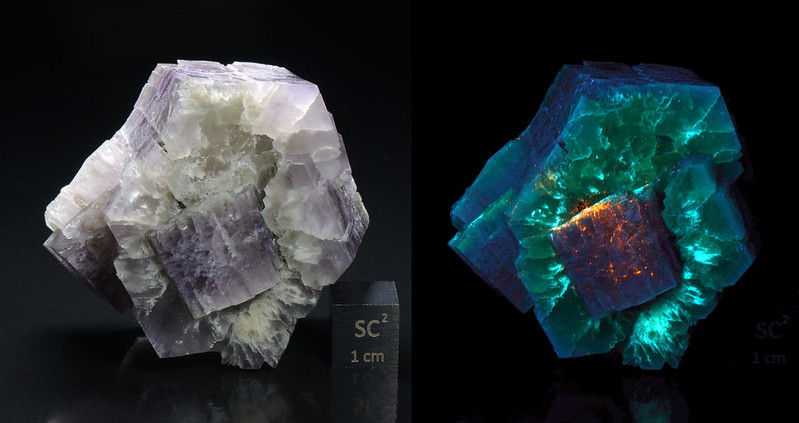
1. Fluorite
Fluorites emit many colors when under UV light but will mostly appear blue, violet, yellow, or green. These colors are most vivid when viewed under long wave ultraviolet light though some specimens can glow without any visible light source.


Fluorite on quartz (image: Stan Celestian)
Fluorite (image: Stan Celestian)
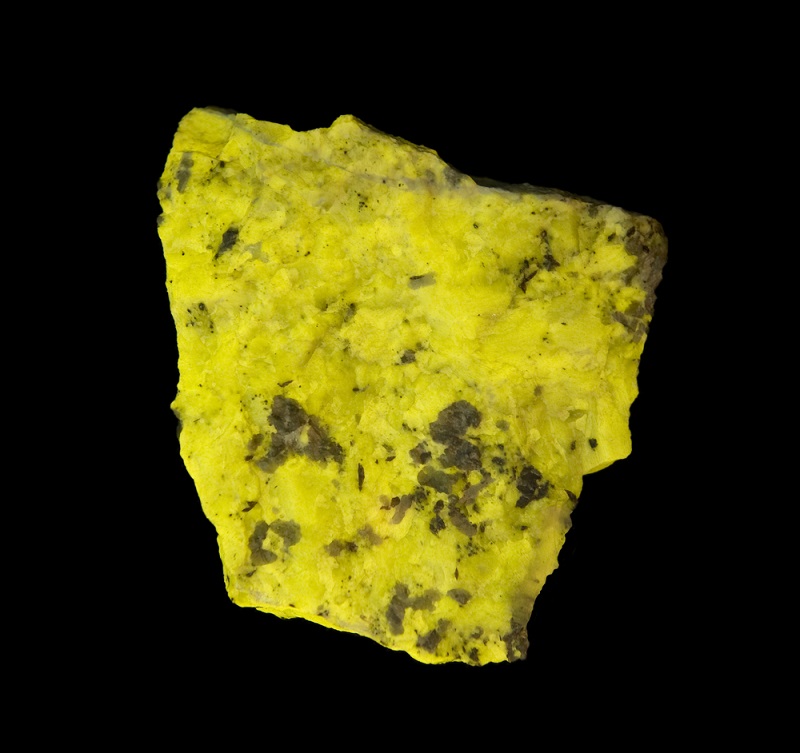
2. Scapolite
Scapolite may not be as well-known as some other minerals, but it offers a unique display under UV light. This mineral typically glows in intense yellow or orange hues when exposed to ultraviolet rays. The fluorescence in scapolite is due to the presence of sulfur, making it a striking example of how chemical elements within minerals react to UV light.

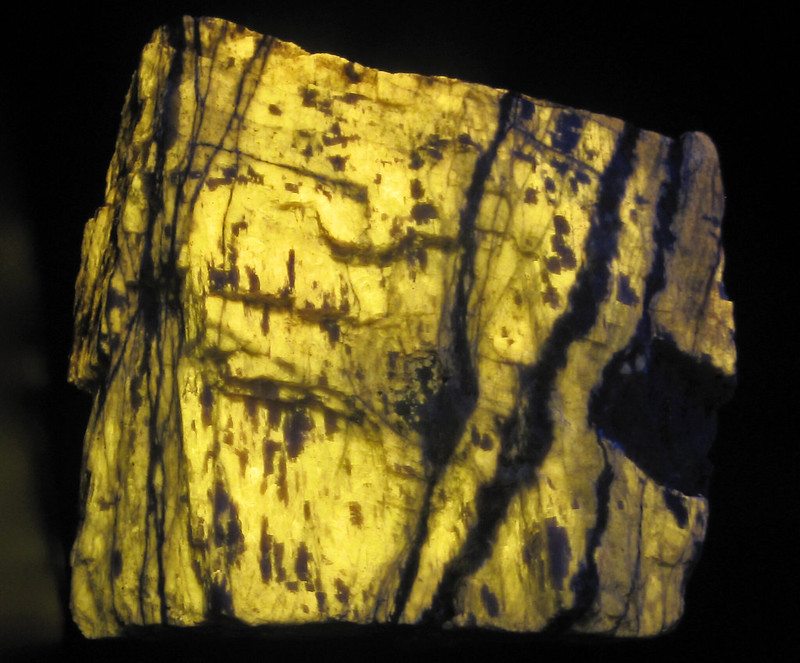
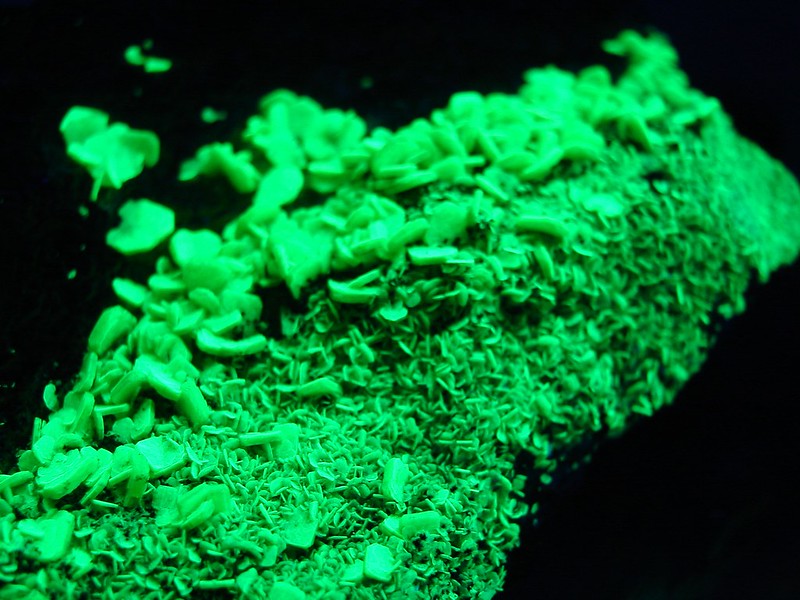
3. Calcite
Calcite is a mineral marvel under UV light, showing a wide spectrum of colors such as red, blue, pink, and sometimes even green depending on the variety. This fluorescence is due to impurities within the calcite, which respond vividly to ultraviolet rays. The diverse range of colors makes calcite not only a favorite among mineral collectors but also a perfect specimen for demonstrating the dramatic effect of UV light on minerals.
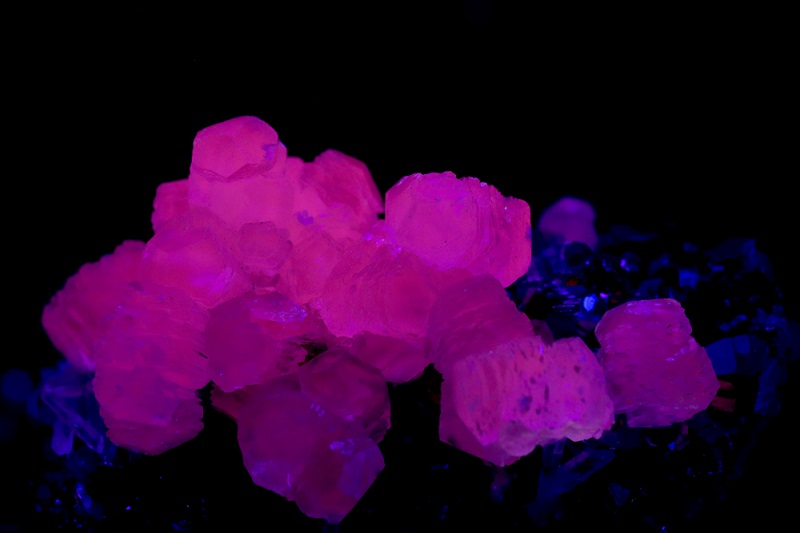


Calcite under UVc (image: Stan Celestian)

Calcite UVC Coals of Fire (image: Stan Celestian)
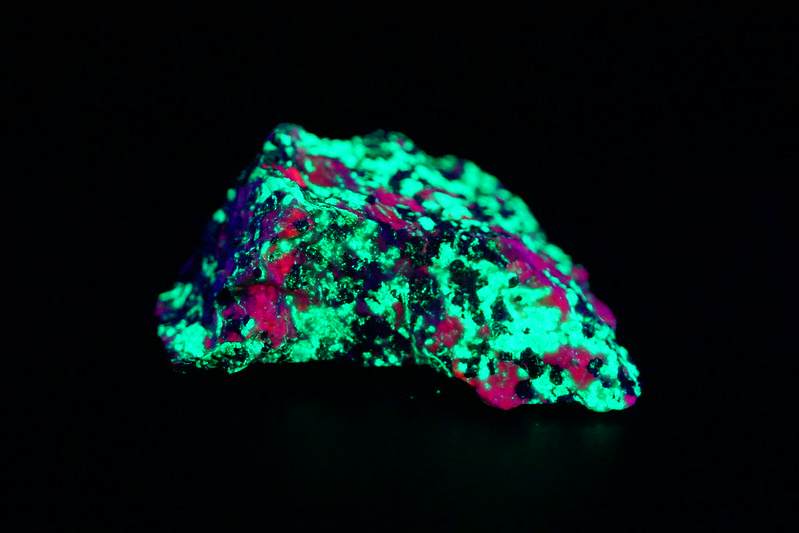
4. Scheelite
Scheelite is renowned for its strong fluorescence under UV light, typically glowing a bright blue or sometimes a yellowish color. This vibrant luminescence is due to the presence of tungsten within the mineral, which reacts vividly to ultraviolet rays.
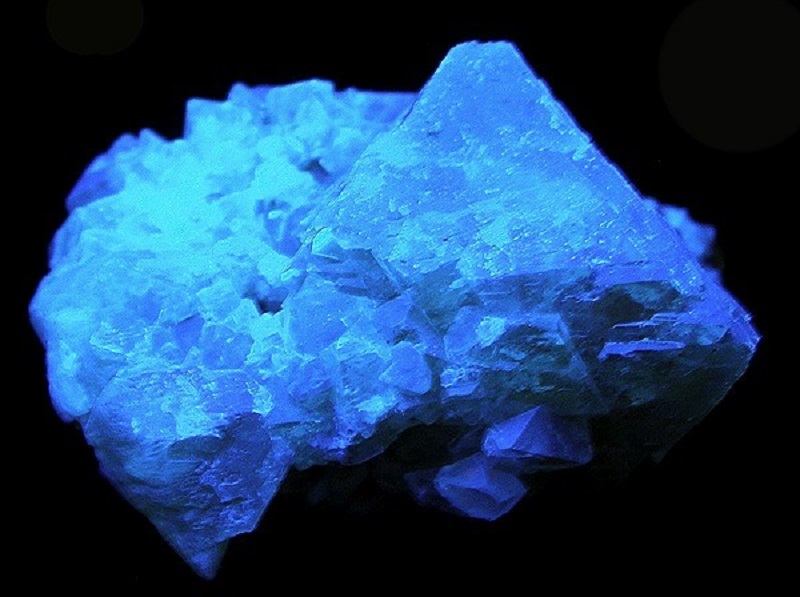


Scheelite under UV (image: Stan Celestian)

Scheelite under UV (image: Stan Celestian)
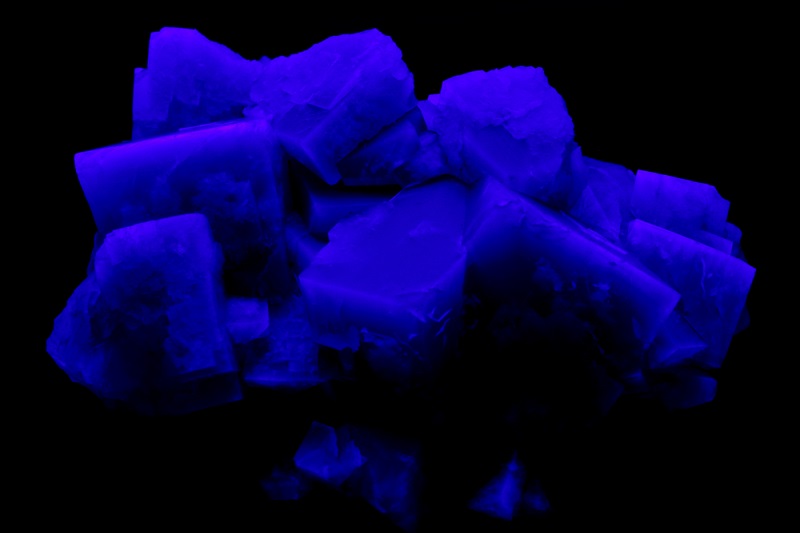
5. Selenite
Selenite, a variety of gypsum, offers a subtle yet mesmerizing fluorescence under UV light, typically emitting a soft, ethereal blue or lime green glow. This gentle luminescence is reflective of selenite’s serene appearance and adds an otherworldly quality to its already striking translucent structure.
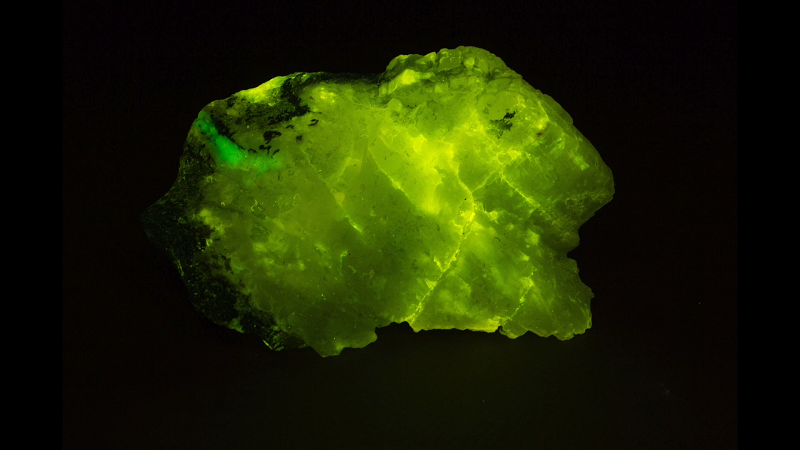


Selenite under UV (image: Stan Celestian)
6. Autunite
Autunite captivates with its intense fluorescent response, glowing a vibrant yellow or green under UV light. This mineral is not just known for its beauty; it’s also a valuable uranium ore. The fluorescence of autunite is particularly notable because it is highly responsive to UV light due to its uranium content, making it a standout in the mineral world
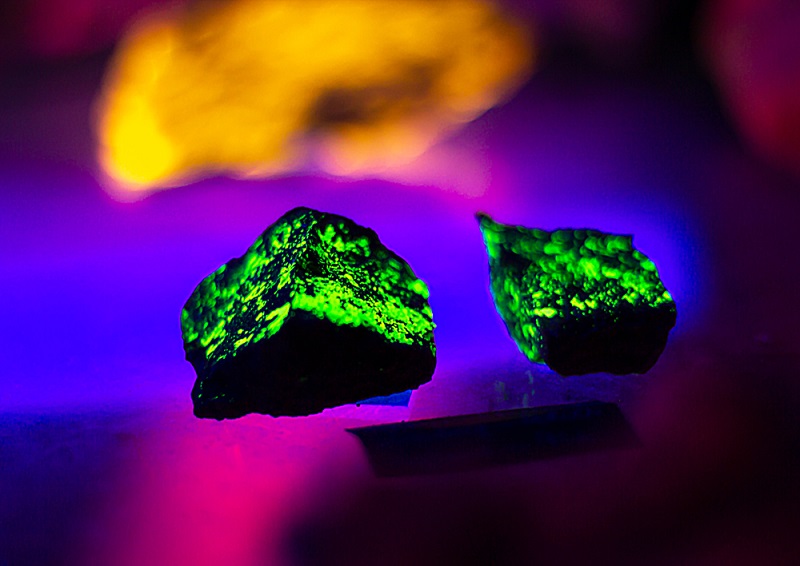
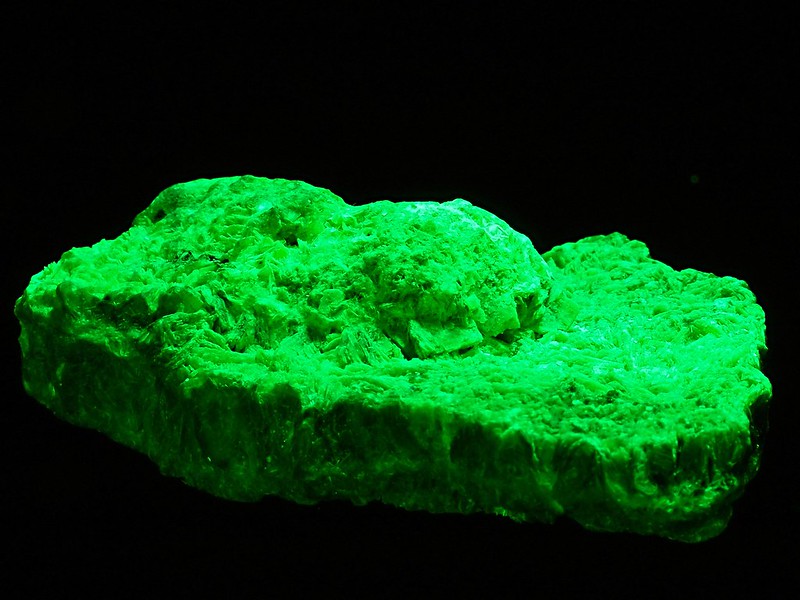


7. Willemite
Willemite is a remarkable mineral known for its intense green fluorescence under UV light. This striking effect is particularly strong due to the presence of zinc silicate, which reacts vividly when exposed to ultraviolet rays. Willemite’s bright green glow makes it a favorite among collectors and a fascinating exhibit in museums showcasing minerals that display fluorescence.
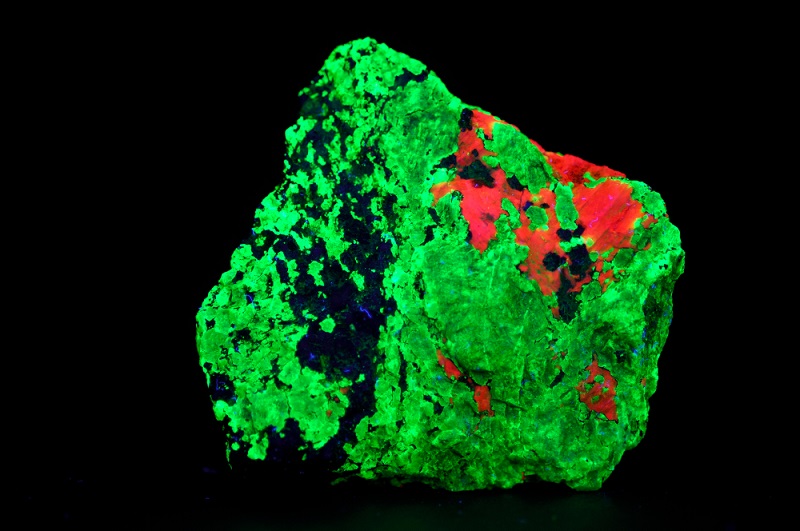

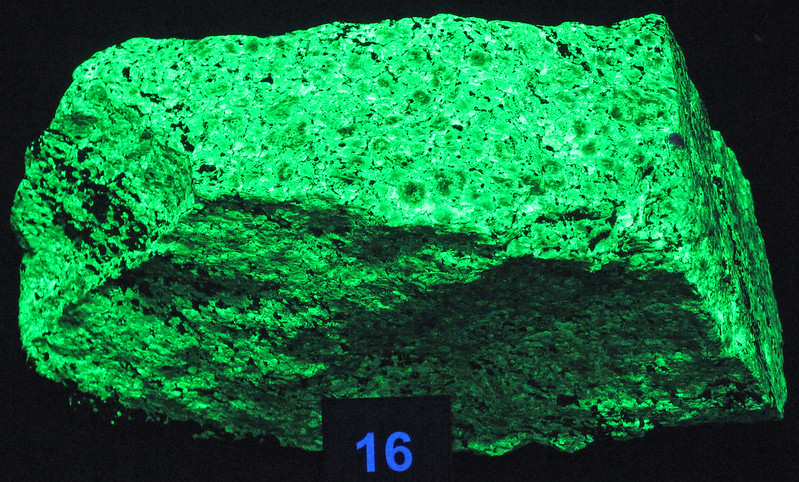
8. Sodalite
Sodalite is a captivating mineral that fluoresces under UV light, typically displaying a vivid orange or red glow. This surprising color shift is due to the presence of sulfur within the mineral, which reacts under ultraviolet light. Known for its rich, royal blue color in normal light, sodalite’s unexpected and striking fluorescence adds an extra layer of intrigue, making it a prized specimen for collectors.
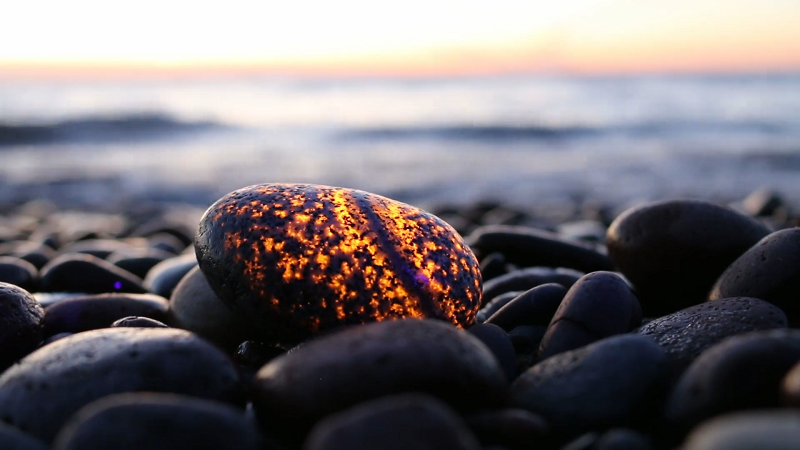

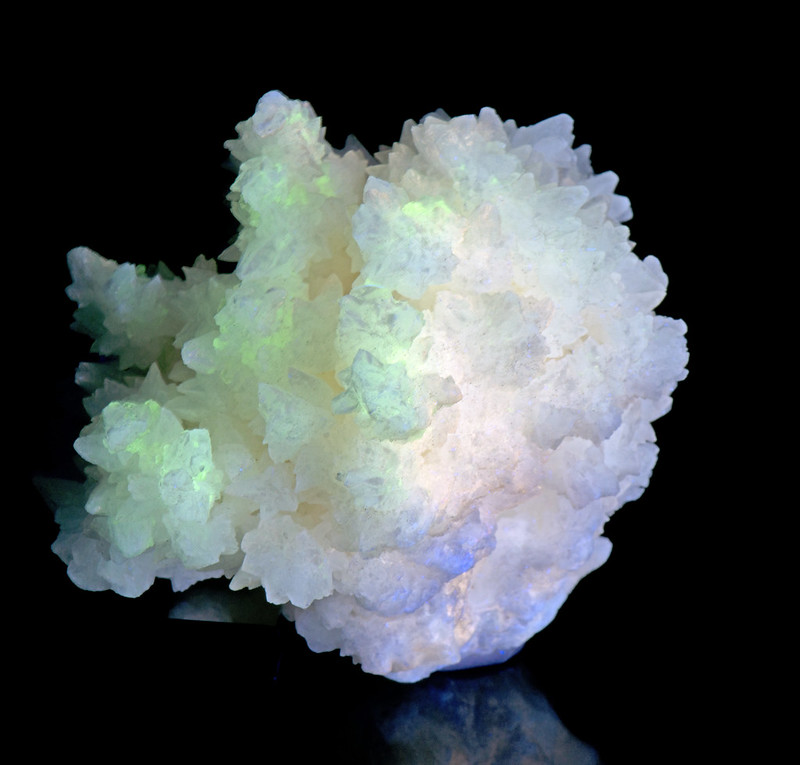
9. Aragonite
Aragonite, a crystal form of calcium carbonate, exhibits a mild but distinct fluorescence under UV light, typically glowing white or light blue. This subtle fluorescence adds an understated elegance to aragonite’s already appealing needle-like crystal formations.
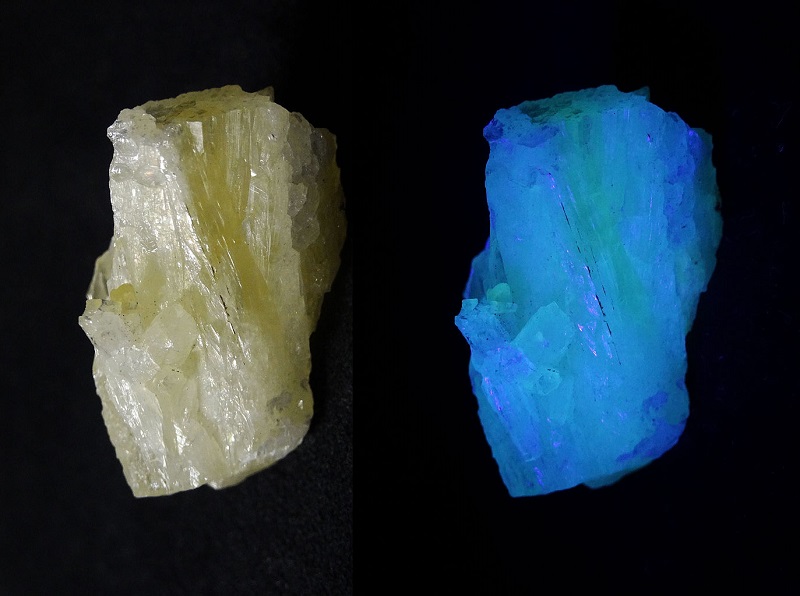


Aragonite (image: Stan Celestian)

Aragonite (image: Stan Celestian)
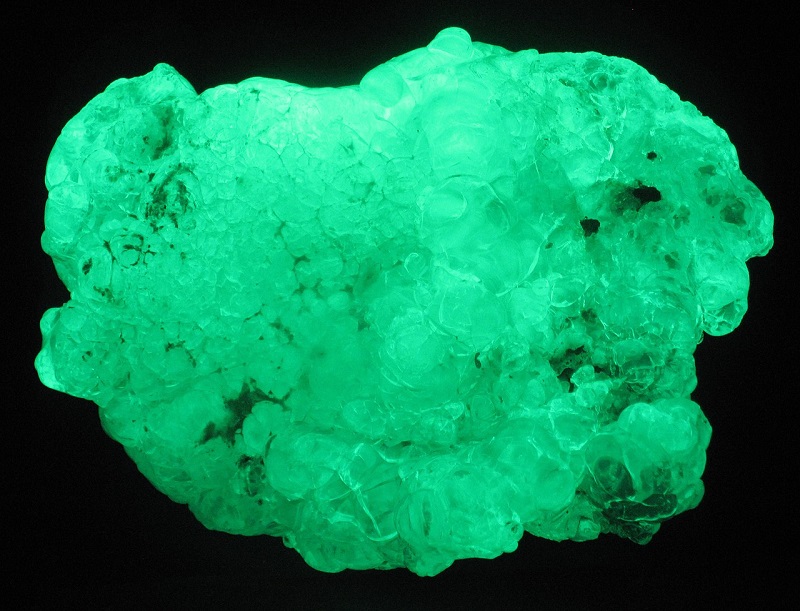
10. Chalcedony
Chalcedony, known for its translucence and waxy luster, sometimes reveals a soft glow under UV light, often emitting a light blue or green fluorescence. This mineral’s subtle fluorescence complements its array of colors, from deep blues to soft pinks and grays.
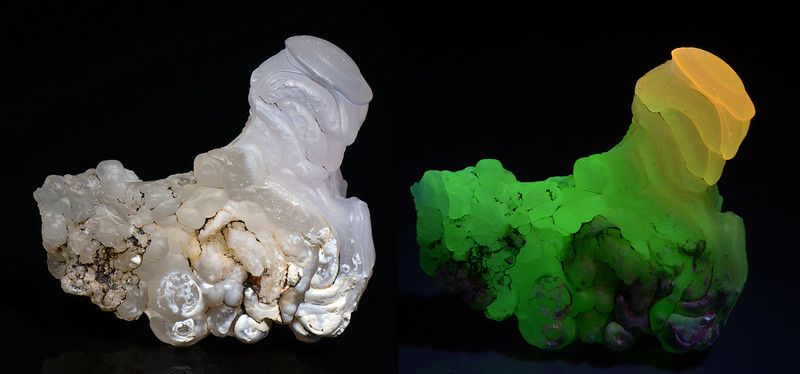

(image: Stan Celestian)

- Online rock and mineral club for collectors of all levels!
- Find community with like-minded rock and mineral enthusiasts.
- Monthly Giveaways!
- Free Access to Entire Digital Library of Products (annual memberships)